Chemical coagulation is a common industrial wastewater solution used by many industrial companies to remove contaminants from their wastewater streams. In this blog post, we’ll explore what chemical coagulation is, how it works, and its limitations and problems.
What is Chemical Coagulation?
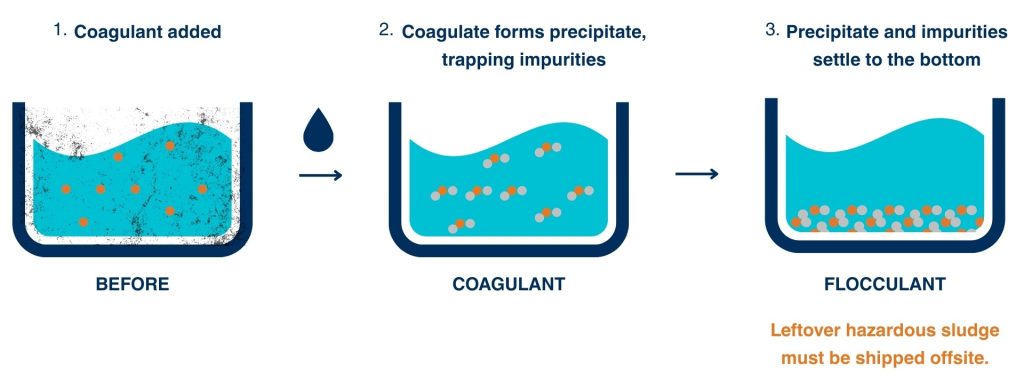
Chemical coagulation is a process that involves adding a coagulant to a wastewater stream, which then in turn forms suspended particles that clump together, forming larger particles that can be removed more easily through settling or filtration. The coagulant is typically a chemical compound that contains positively charged ions, which attract negatively charged particles in the wastewater. When the coagulant forms suspended particles, it is also effective at precipitating other dissolved metallic compounds.
How Chemical Coagulation Works
In chemical coagulation, the coagulant is added to the wastewater stream, causing the formation of flocs, which are larger particles made up of the contaminants in the wastewater. The flocs are then removed through settling or filtration, leaving behind a cleaner water stream. The choice of coagulant depends on the type of contaminants in the wastewater, the pH of the water, and other factors. Common coagulants include aluminum sulfate, ferric chloride, and polyaluminum chloride.
Limitations and Problems with Chemical Coagulation
While chemical coagulation is a popular industrial wastewater treatment method, it comes with several limitations and problems. One major limitation is the production of a waste stream, often in the form of a sludge, which must be shipped offsite for disposal. This sludge disposal process can be costly and time-consuming for companies. Additionally, chemical coagulation can be ineffective for certain contaminants, such as low concentration dissolved metals or organic compounds, and may require additional treatment steps, such as filtration or ion exchange, to remove these contaminants down to the concentrations required for water discharge from the facility. Finally, chemical coagulation can be expensive and energy-intensive.
ElectraMet: A Better Solution
At ElectraMet, we offer a better solution that eliminates the need for chemical coagulation and produces no waste stream. Our solution is entirely new, chemical-free, uses low amounts of power, and takes up a small footprint in an industrial complex. With ElectraMet, we can return the metal as a pure sheet or metal oxide to the customer, eliminating the need for costly waste disposal and producing a higher quality product that is more desirable for industrial applications.
Conclusion
Chemical coagulation is a common water treatment process used by many industrial companies to remove contaminants from their wastewater streams. However, it comes with several limitations and problems that can make it costly and difficult to manage. At ElectraMet, we offer a better solution that eliminates the need for chemical coagulation, producing no waste stream, and providing a more efficient and cost-effective solution for industrial wastewater treatment.
